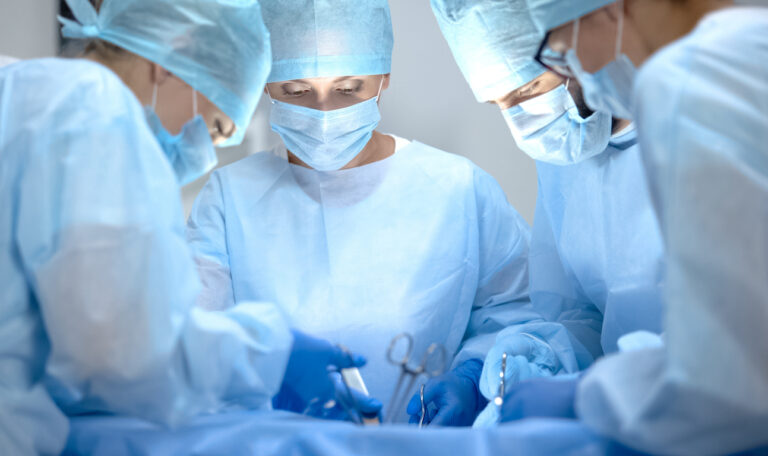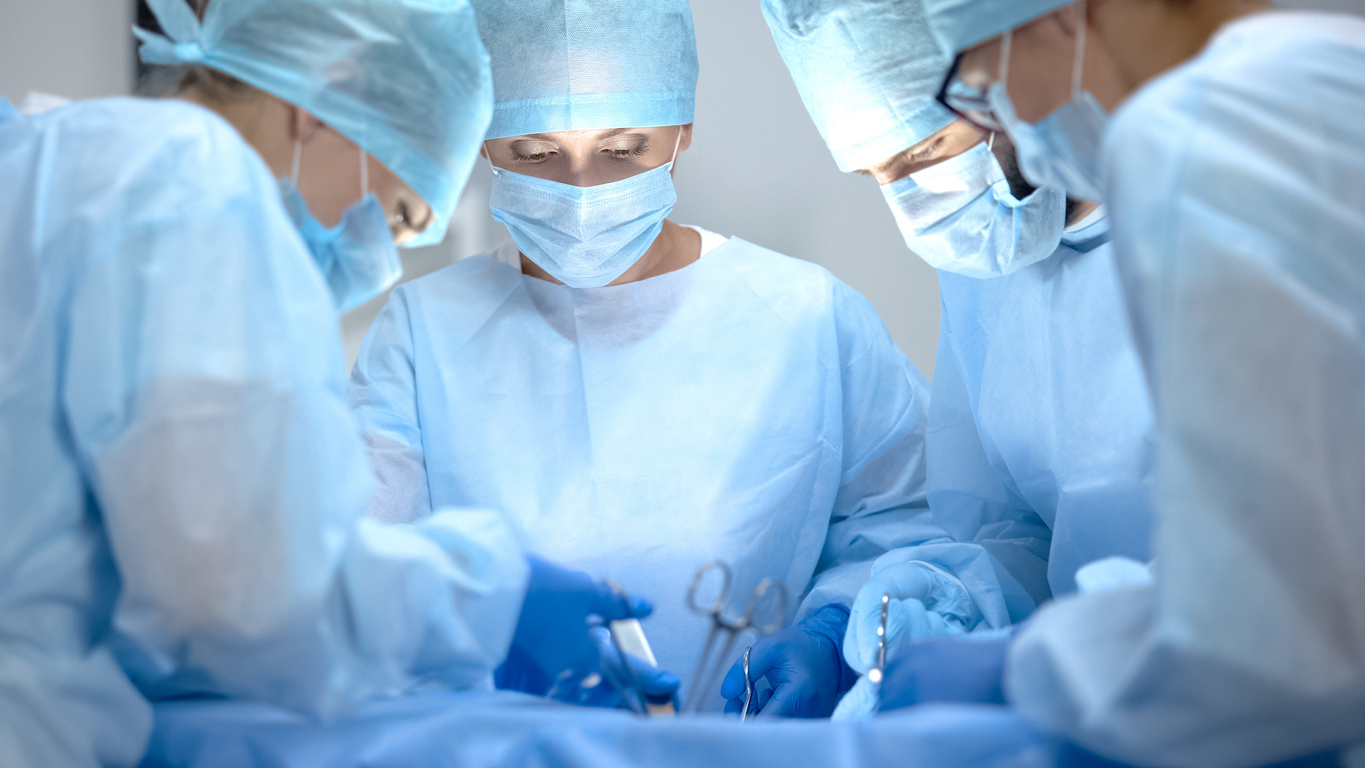
The stories are frequent enough; surgical sponge left inside patient. Surgeon leaves forceps in abdomen. 3 foot guide wire found in patients’ chest. Retained surgical items can include sponges, towels, medical device components, surgical instruments, needles, scalpel blades and entire instruments.
They can be discovered months or even years after the initial procedure and cause significant morbidity, serious infection and mortality. The risk is higher for obese patients, during abdominal surgery and lengthy operations involving multiple surgical teams. The risk for retained items is 9-fold higher during emergency surgeries and 4-fold higher when an unexpected change of procedure takes place.